In the ever-evolving world of shared power banks, the choice between slow charging and fast charging can significantly impact both user satisfaction and business operations. Fast charging enhances customer satisfaction and convenience by allowing users to quickly recharge their devices. Slow charging, on the other hand, offers a more cost-effective option and encourages longer customer stays. So, which option is the best for your business?
In this article, we’ll break down the differences between slow and fast charging shared power banks, exploring factors like speed, customer preferences, market trends, and the impact on your bottom line. We’ll also provide insights into how each solution could be better suited to specific business models, helping you make an informed decision.
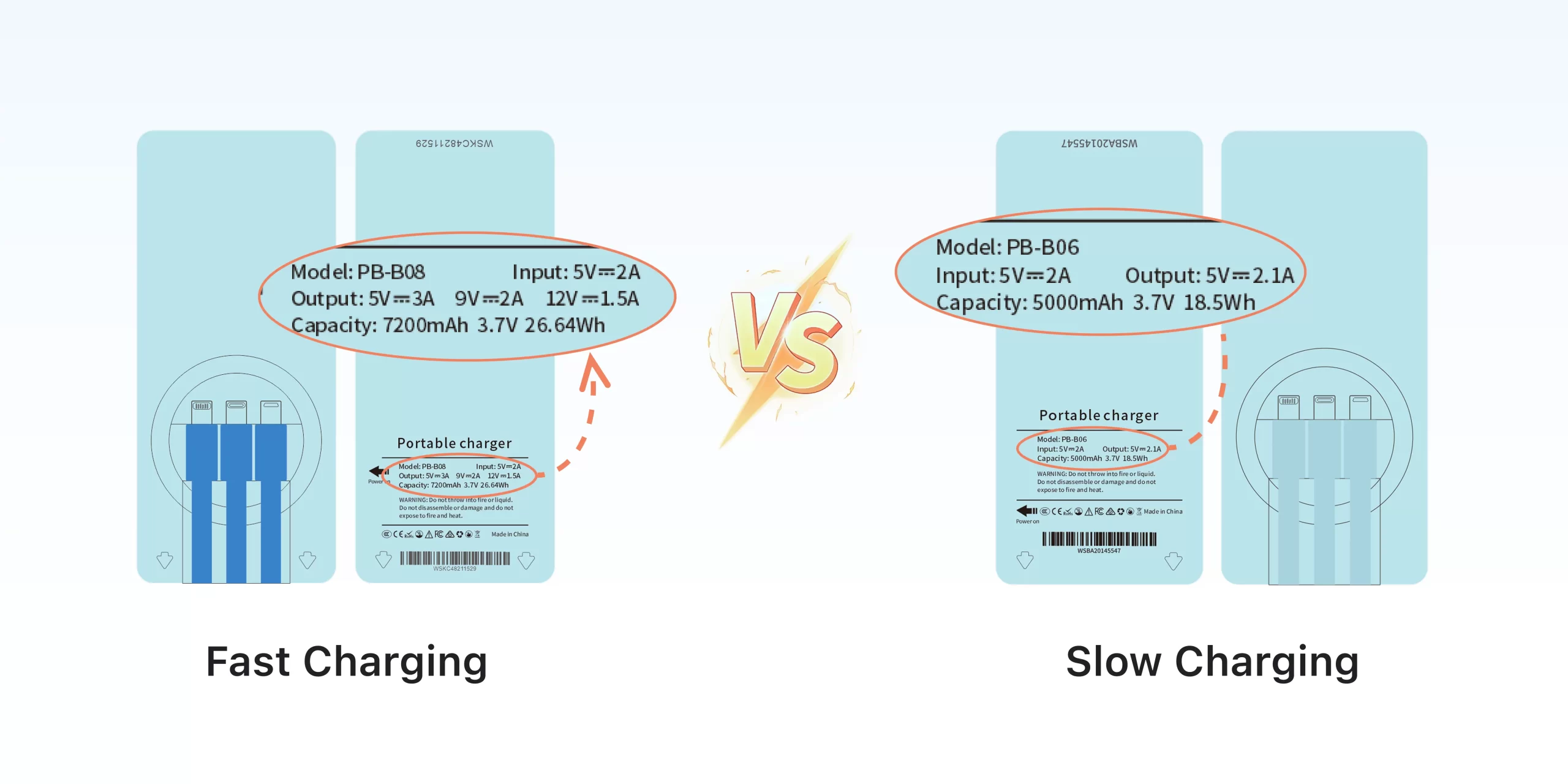
Table of Contents
Part1. How Fast Charging Works
What is Fast Charging?
Fast charging refers to technologies that deliver a higher power output—typically 18W or more—allowing devices to charge much faster than traditional methods.
Requirements for Fast Charging
For fast charging to work effectively, both the power bank and the user’s device must support compatible fast charging protocols, such as Qualcomm Quick Charge or USB Power Delivery (USB-PD). If either component lacks this capability, the charging speed reverts to slow rates.
Charging Speed Comparison
To illustrate the difference, let’s compare a typical slow charging power bank with a fast charging one:
| Feature | Slow Charging Power Bank | Fast Charging Power Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Input | 5V⎓2A | 5V⎓2A |
| Output | 5V⎓2.1A | 5V⎓3A, 9V⎓2A, 12V⎓1.5A |
| Capacity | 5000mAh | 7200mAh |
| Max Power Output | ~10W | ~18W |
When charging an iPhone 13, the speed can make a big difference. Using a slow 10-watt charger, the phone reaches about 30% battery in 30 minutes. However, with a fast 18-watt charger, it can charge to 50-60% in the same time. This means that fast charging is up to 80-100% more time-efficient.
Part2. Pros and Cons of Fast Charging
As fast charging becomes increasingly popular, it’s important to weigh both its benefits and drawbacks. While faster charging speeds can enhance customer satisfaction and boost revenue, they also come with higher costs and operational challenges. Let’s explore the key advantages and potential downsides of adopting fast-charging shared power banks.
2.1 Advantages
1. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Fast charging caters to customers with limited time or urgent charging needs. The ability to quickly recharge a device—such as during a short coffee break—can greatly enhance customer satisfaction and foster loyalty.
2. New Competitive Edge
By offering fast charging, businesses can differentiate themselves through service quality rather than competing solely on price. This differentiation helps companies stand out in the market, appealing to customers who value speed and efficiency.
2.2 Disadvantages
1. Higher Initial Investment and Maintenance Costs
Fast charging power banks require more expensive hardware, leading to higher initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs. Additionally, the increased power output accelerates battery wear, necessitating more frequent replacements.
2. Pricing Challenges
To offset the higher costs, operators often raise rental fees for fast charging units. This may result in a perceived disadvantage, especially among price-sensitive customers who only need a minimal charge, such as those looking to power up for just a short while. It may also discourage users with devices that do not support fast charging, as they might feel the service does not justify the cost.
Part3. Ideal Business Scenarios for Slow and Fast Charging
Choosing between slow and fast charging isn’t just about speed—it’s about aligning with the right business environment. Different locations and customer behaviors influence whether slow or fast charging will be more profitable. Below, we analyze which types of businesses benefit most from each option.
3.1 Slow Charging
1. Low-Traffic Venues
Fast charging enables more users to utilize the service in a shorter period, reducing congestion at charging stations and enhancing convenience. This not only enhances the customer experience but also increases overall usage rates. Moreover, in high-traffic areas, users are more willing to pay a premium for fast charging, as they prioritize efficiency over cost.
2. Long-Stay Locations
In bookstores, gyms, or cafes, slow charging encourages customers to linger. A device charging slowly over an hour might prompt an extra coffee order or extended browsing, increasing on-site spending.
3.2 Fast Charging
1. High-Traffic Areas
Fast charging enables more users to utilize the service in a shorter period, reducing congestion at charging stations and enhancing convenience. This not only enhances the customer experience but also increases overall usage rates. Moreover, in high-traffic areas, users are more willing to pay a premium for fast charging, as they prioritize efficiency over cost.
2. Emergency Charging Needs
In urgent situations where every minute counts, fast charging shared power banks become essential. Airports, hospitals, and business centers often require quick recharges, whether to stay reachable, access important updates, or continue working. Fast chargers deliver the quick power boost needed to meet these time-sensitive needs.

Part4. Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
1. Current Market Share of Fast and Slow Charging Power Banks
According to a report by SNS Insider, the shared power bank market is increasingly leaning toward fast charging. Growing consumer demand for speed and convenience is driving this trend, with fast charging power banks expected to dominate the market in the coming years.
2. Long-Term Profitability and Return on Investment (ROI)
While fast charging stations require a higher initial investment, they can deliver greater profitability due to increased revenue and consumers’ willingness to pay for convenience. However, in low-traffic areas with lower operating costs, slow-charging stations may offer a better long-term return on investment.
3. Consumer Willingness to Pay
Consumers are generally willing to pay a premium for faster charging, especially in time-sensitive environments. However, businesses must carefully assess local market conditions to determine whether charging customers extra can offset the additional costs. In markets where shared power banks are already well-established, companies may consider adopting a competitive pricing strategy—offering fast charging at the same price as slow charging in the early stages—to gain market share.
Conclusion
Deciding between slow and fast charging shared power banks hinges on your business’s unique needs, target audience, and operational context. Fast charging shines in high-traffic, time-critical environments, offering a premium service that boosts customer satisfaction and rental frequency—albeit at a higher cost. Slow charging, by contrast, is a budget-friendly choice for low-traffic or long-stay venues, fostering extended engagement and steady returns.
The optimal approach depends on aligning your customers’ needs with your financial objectives. By weighing the trade-offs—speed versus cost, convenience versus simplicity—and staying attuned to market shifts, you can deploy a shared power bank solution that maximizes both user experience and your bottom line.
HeyCharge‘s business spans multiple countries. Whether you’re looking to understand local market conditions or learn more about shared power banks, feel free to contact us!



